Remember those confusing diagrams of cell membranes with arrows pointing in and out, representing molecules moving across? That’s cell transport, a vital process for all living things. I used to struggle with this concept until I stumbled upon the Amoeba Sisters’ videos! They break down complex biological processes into digestible, relatable chunks. Their video on cell transport was a game-changer for me, simplifying the concept and making it stick in my memory. If you’re also trying to get a handle on cell transport, you’ve come to the right place. This article will serve as your guide to understanding cell transport using the Amoeba Sisters’ video recap as a springboard.
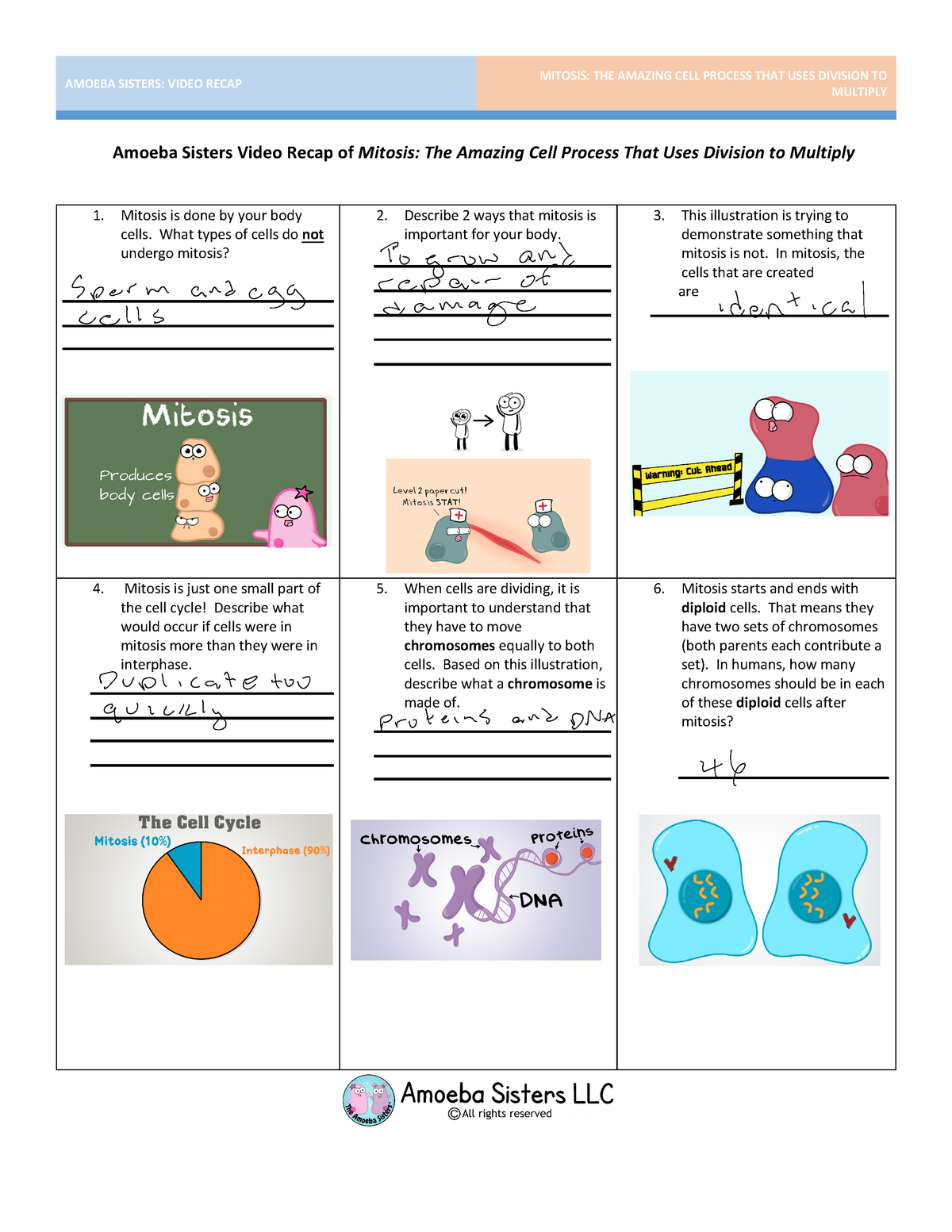
Image: www.studocu.com
By the end of this article, you’ll have a solid grasp of the key concepts of cell transport, including passive transport like diffusion and osmosis, and active transport, which requires energy. We’ll explore the role of the cell membrane in regulating what enters and exits the cell, and how various transport mechanisms contribute to maintaining a stable internal environment.
Understanding the Basics of Cell Transport
The cell membrane, a thin layer that surrounds every cell, acts like a selective barrier, controlling the movement of substances in and out. This movement is called cell transport. Imagine it like a bustling city gate: some people (molecules) can walk through freely, while others need special access or even a ride. That’s basically how cell transport works.
Now, there are two primary modes of cell transport: passive transport and active transport. Passive transport is like coasting downhill on a bike – it doesn’t require any energy. Molecules move from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration, driven by the natural flow of things. Active transport, on the other hand, is like biking uphill – it needs energy to move molecules against their concentration gradient, from areas of lower concentration to areas of higher concentration.
Delving Deeper into Passive Transport
Passive transport encompasses several important processes:
- Diffusion: Imagine dropping a drop of food coloring into a glass of water. The color spreads out until it’s evenly distributed. That’s diffusion- the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Think of it as molecules spreading out to create a more even distribution.
- Osmosis: This is a special type of diffusion where the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane (like the cell membrane) is driven by the difference in water concentration. Water moves from a region of higher water concentration (lower solute concentration) to a region of lower water concentration (higher solute concentration) to try and equalize the concentration on both sides.
- Facilitated Diffusion: Sometimes molecules are too large or too charged to easily cross the cell membrane. That’s where facilitated diffusion comes in. In this process, membrane proteins act as “helpers” or “carriers,” guiding these molecules across the membrane without requiring energy. This is like using a special lane on a highway for specific types of vehicles.
Active Transport: Moving Molecules Against the Flow
Active transport mechanisms require energy expenditure, often from ATP, which acts as the cell’s energy currency. Here are two key processes under active transport:
- Protein Pumps: Think of these like tiny motors embedded within the cell membrane that use energy to move molecules against their concentration gradient. You can visualize these protein pumps as active transporters that “pump” molecules from a low concentration area to a high concentration area, requiring a source of energy to do so.
- Bulk Transport: For larger molecules or even entire cells, active transport employs special mechanisms to move them across the membrane. This is like a cargo ship transporting goods across a large body of water. Two major processes fall under bulk transport: endocytosis (bringing substances into the cell) and exocytosis (releasing substances from the cell).

Image: www.teacherspayteachers.com
The Amoeba Sisters: Making Cell Transport Fun and Easy
The Amoeba Sisters are known for their engaging and informative videos that explain complex scientific concepts in a simple and relatable way. Their video on cell transport is no exception. They use captivating animations, relatable analogies, and a touch of humor to make the learning process enjoyable.
The Amoeba Sisters’ video recap of cell transport provides a comprehensive overview of the topic, including:
- Defining the key terms: The video clearly defines important terms like cell membrane, passive transport, active transport, diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion.
- Illustrating the different types of transport: Through clear animations, the video visually explains how different molecules move across the cell membrane.
- Highlighting the importance of cell transport: The video emphasizes how vital cell transport is for maintaining cell function, including nutrient uptake, waste removal, and communication between cells.
Tips and Expert Advice for Mastering Cell Transport
Now that we’ve delved into the basics, here are some tips for cementing your understanding of cell transport:
- Watch the Amoeba Sisters’ video multiple times: Repetition is key to understanding and retaining information. Watching the Amoeba Sisters’ video a few times will help you grasp the concepts and familiarize yourself with the terminology.
- Take notes and draw diagrams: Actively engaging with the information by taking notes and sketching diagrams enhances comprehension and makes the learning process more interactive.
- Create flashcards or use online quizzes: Flashcards and quizzes are effective tools for testing your knowledge and strengthening your memory. They provide a concise way to review key concepts and definitions.
- Apply cell transport to real-life examples: Think of how cell transport works in your own body, such as digestion and the uptake of nutrients from your food. Relating biological processes to everyday phenomena helps solidify your understanding.
- Ask questions: Don’t be afraid to ask questions if you encounter any areas of confusion. Seek clarification from your teacher, a tutor, or online resources.
FAQ: Your Cell Transport Questions Answered
Here are some frequently asked questions about cell transport.
Q: What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis?
A: Both diffusion and osmosis are types of passive transport. Diffusion involves the movement of any type of molecule from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Osmosis, on the other hand, specifically refers to the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane, driven by the concentration gradient of water.
Q: Why is active transport important?
A: Active transport is crucial for maintaining a stable internal environment within cells. It allows cells to concentrate essential molecules (like glucose, ions, and amino acids) inside the cell, even when the concentration outside the cell is lower. This is important for cellular function, maintaining proper osmotic balance, and carrying out processes like nerve impulse transmission.
Q: How does the cell membrane regulate cell transport?
A: The cell membrane acts as a selectively permeable barrier, allowing certain substances to pass through while restricting others. This selective permeability is determined by the structure of the membrane, which comprises a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. These proteins act as channels, carriers, or pumps, regulating the flow of various molecules across the membrane.
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap Of Cell Transport Answer Key
Conclusion
Understanding cell transport is fundamental to grasping the complexities of life at the cellular level. The Amoeba Sisters’ video recap is a fantastic resource for mastering this concept, providing a clear, engaging, and memorable introduction to the world of cell membrane movement. By watching the video, reviewing the key terms, and applying your knowledge to real-life examples, you can become confident in your understanding of this important process.
Are you interested in exploring more about cell transport or diving into other fascinating biological topics? Leave your thoughts and questions in the comments below. I’m excited to continue this discussion with you!






