Ever wondered how your computer “sees” other devices on your network, like your phone, printer, or even the smart refrigerator in the kitchen? It’s a process that happens under the hood, a silent dance of data packets travelling through cables and wireless waves. This invisible communication, a fundamental aspect of networking, involves something called network scanning, and understanding it can be the key to unlocking a deeper understanding of how our digital world communicates.
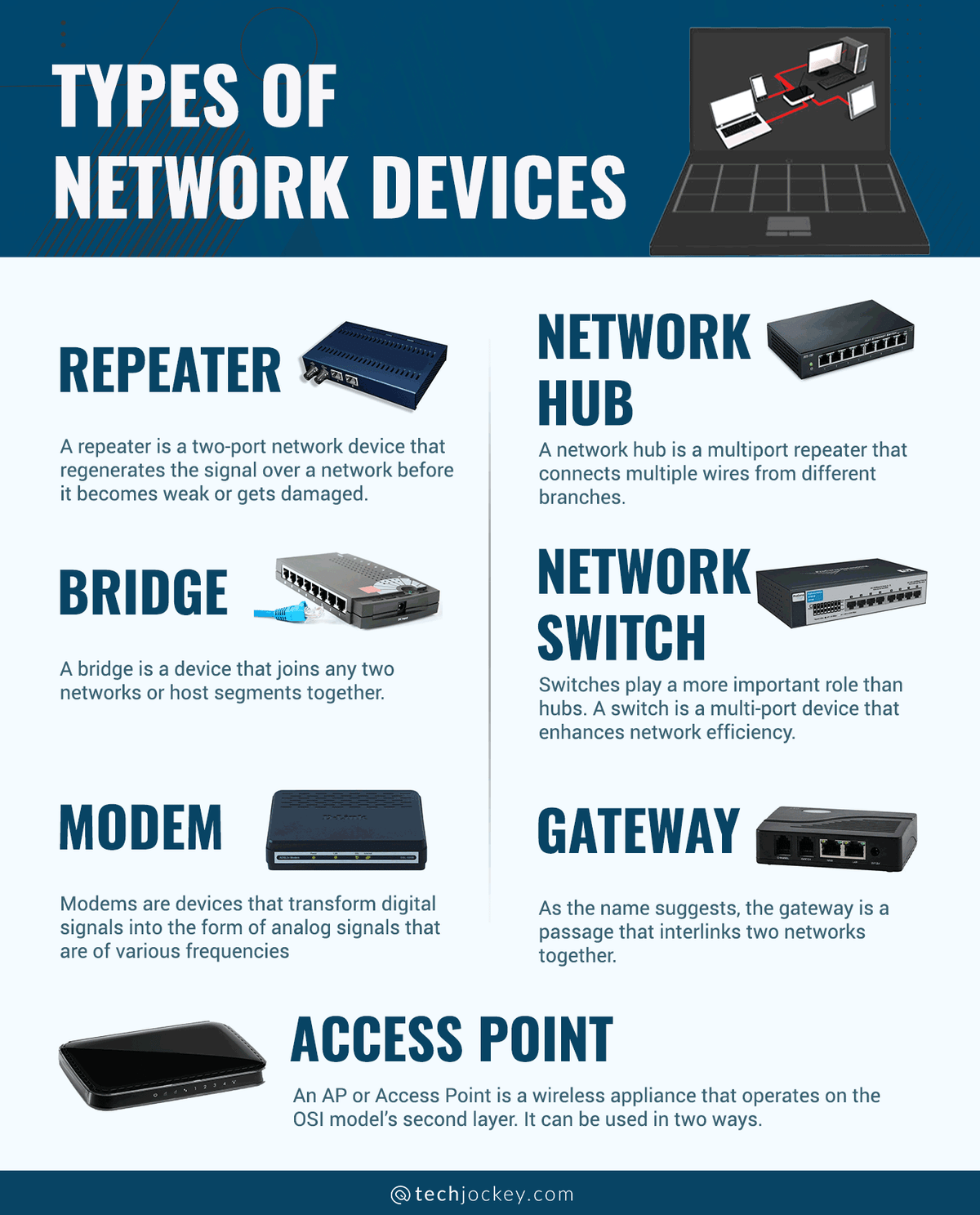
Image: ar.inspiredpencil.com
In this software lab simulation, “19-1: Scanning a Network for Connected Devices,” we’ll delve into the fascinating world of network exploration. You’ll learn the basics of network scanning, how it works, and its various applications, both for good and for potentially malicious purposes. Get ready to explore the hidden pathways of your network and gain valuable insights into the invisible forces that keep our devices connected.
Understanding Your Network: The Foundation of Scanning
The Invisible Fabric: Network Basics
Imagine a city bustling with activity, but instead of people, it’s data flowing between devices. This is a network, a system of interconnected devices that can share information with each other. In a home network, these devices could be anything from a laptop to a smart TV, a game console, or a network printer. Each device has a unique address, like a street address in the digital city.
The Map: IP Addresses
Network devices communicate with each other using a system of “addresses,” called IP addresses. These addresses are like unique identifiers for each device on the network. Imagine the IP address as a device’s postal code, allowing data to be delivered to the right recipient. In a home network, your router acts as a central hub, assigning these IP addresses to connected devices.
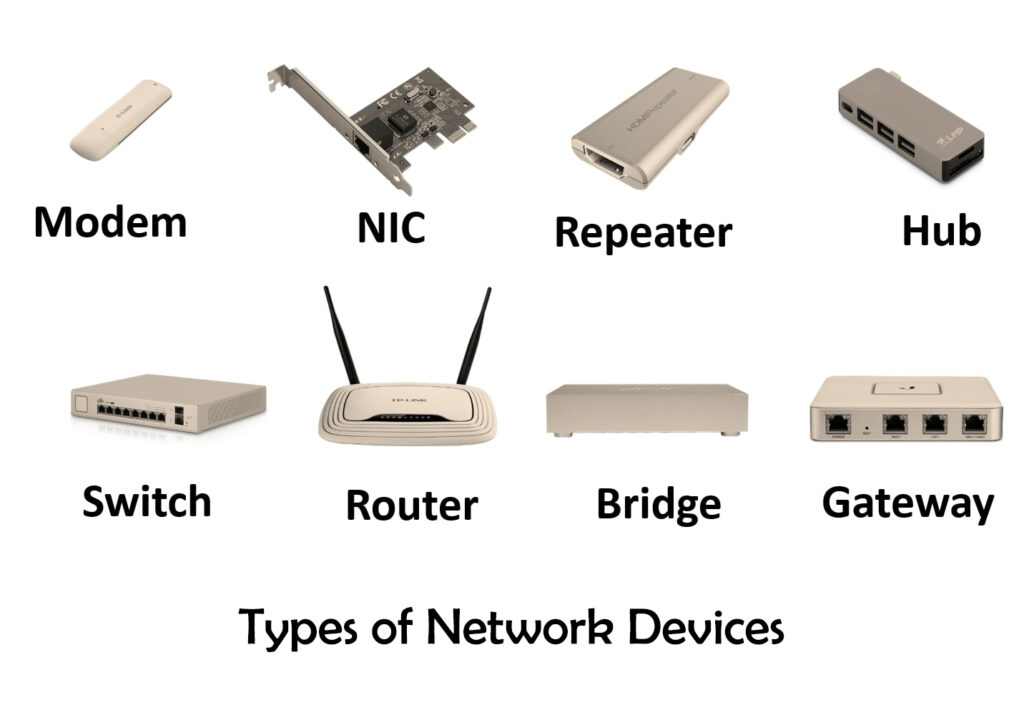
Image: www.itrelease.com
The Tools of Exploration: Network Scanning Techniques
Active Scanning: Sending Out Signals
Active network scanning involves sending out special packets called “probes” across the network. These probes are like little messengers, asking devices if they are present and listening. If a device responds to the probe, you know that it’s alive and connected to the network. Commonly used tools for active scanning include nmap and ping.
Passive Scanning: Listening at the Crossroads
Passive scanning operates differently, instead of sending out messages, it listens to the communication already happening on the network. This is like eavesdropping on conversations in the digital city, gathering information about active devices and the services they offer. Examples of passive scanning techniques include packet analysis and network monitoring.
Port Scanning: Deciphering Services
Imagine each device on the network having a small shop, offering specific services. Port scanning attempts to identify these services by sending probes to specific ports, or virtual doorways, on each device. This can reveal what kind of applications are running, whether it’s a web server, a file sharing service, or even a gaming application.
The Applications of Network Scanning: From Security to Troubleshooting
Security Analysis: Identifying Vulnerabilities
Network scanning is crucial for security professionals who need to identify devices that might be vulnerable to attack. By scanning the network, security experts can identify devices that are running outdated software or have open ports that could be exploited. This helps them to patch vulnerabilities and protect the network from malicious actors.
Network Inventory Management: Tracking Devices
IT administrators often use network scanning to keep track of all devices connected to a network. This information helps them to manage devices effectively, update software, troubleshoot problems, and ensure that the network is running smoothly.
Troubleshooting Network Issues: Diagnosing Problems
When network problems arise, network scanning can be used to pinpoint the source of the problem. By identifying devices that are not responding, network administrators can quickly isolate the issue and resolve it efficiently.
Beyond the Lab Simulation: The Real-World Applications of Network Scanning
The Dark Side: Malicious Network Scanning
While network scanning has legitimate uses, it can be also used maliciously. Hackers can use scanning techniques to identify vulnerable devices, steal sensitive information, or launch attacks on a network. This is why it’s important to use network scanning tools responsibly and to implement security measures to protect your network.
The Future of Networking: Automation and Machine Learning
The field of network scanning is constantly evolving, with new techniques and tools emerging regularly. Automation and machine learning are playing increasingly important roles in network scanning, providing new ways to analyze large amounts of data and identify hidden patterns.
Software Lab Simulation 19-1: Scanning A Network For Connected Devices
The Importance of Understanding Network Scanning
By understanding the concepts and techniques behind network scanning, you can gain a much deeper appreciation for how our digital world operates. Whether you are interested in cybersecurity, network administration, or simply want to learn more about the technology that surrounds us, network scanning is a topic that is worth exploring. It is a key to understanding the invisible forces that keep our devices connected and our digital lives thriving.






