Have you ever wondered why your phone gets hot when you use it for a long time? Or why a roller coaster zooms down a hill and then slowly climbs back up the next? The answer lies in a fundamental principle of physics known as the law of conservation of energy. This law states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. This seemingly simple concept has profound implications for everything from understanding the workings of the universe to designing energy-efficient appliances.
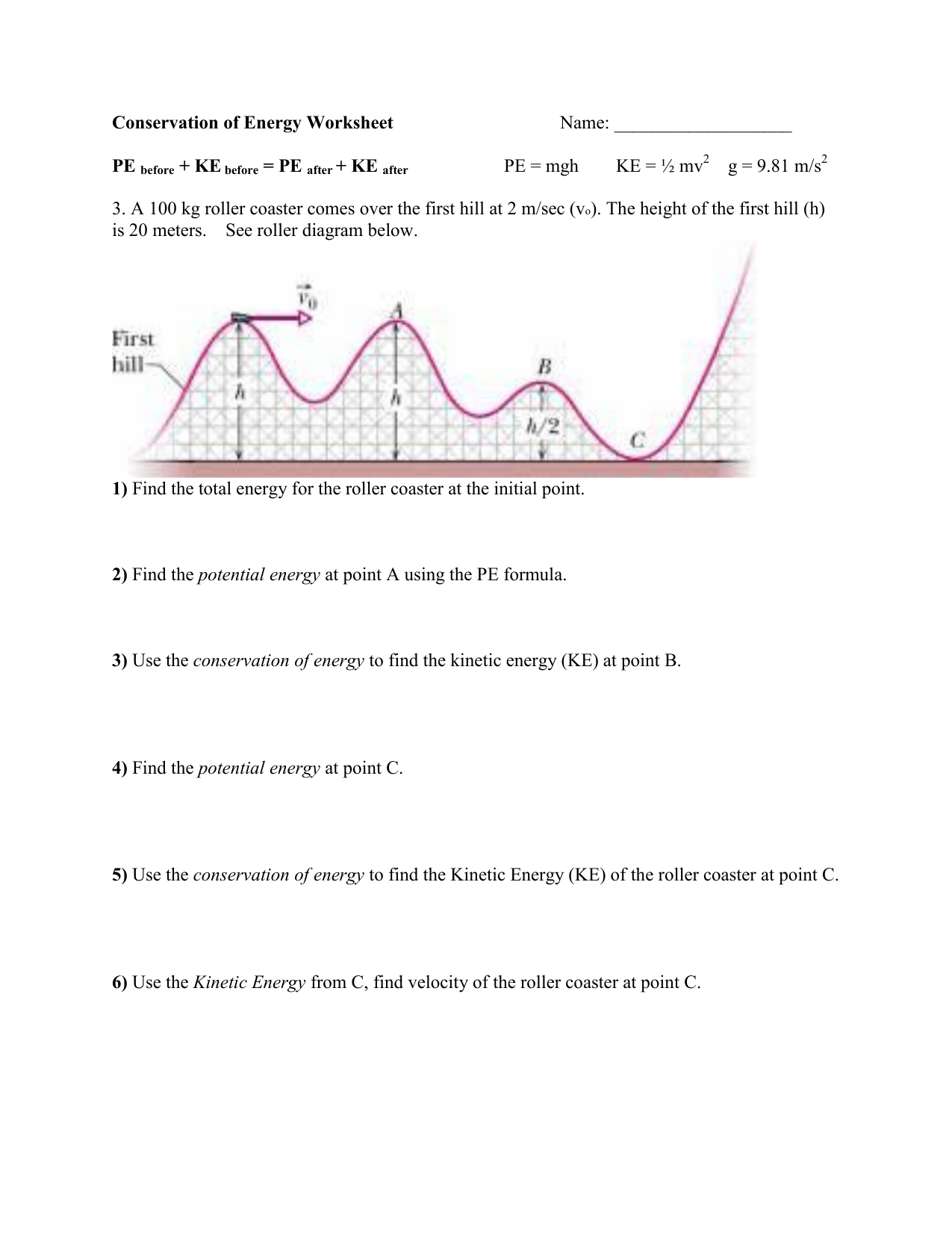
Image: imsyaf.com
Conservation of energy is a cornerstone of physics, underpinning our understanding of how the world works. It’s not just something you learn in school but a principle we use every day. Whether you’re turning on a light bulb, riding a bicycle, or simply taking a walk, energy is constantly being transformed and transferred. To grasp the essential concepts of energy, its various forms, and how it’s conserved, students often rely on worksheets. But what about the answer key that unlocks those crucial principles? Dive deeper into the world of conservation of energy with a focus on the answers that illuminate the key concepts.
Understanding the Basics: Building a Foundation
Before exploring the specifics of the conservation of energy worksheet answer key, it’s crucial to lay a strong foundation by understanding the fundamental concepts. Energy itself is the ability to do work. Work, in a physics context, is the application of force over a distance. In essence, an object possessing energy has the capacity to exert a force to move things. Familiarize yourself with the common forms of energy:
Forms of Energy
- Kinetic Energy: The energy of motion. Think of a moving car or a spinning top. The faster the object moves, the more kinetic energy it possesses.
- Potential Energy: Stored energy based on an object’s position or condition. Picture a rock perched on a cliff. This rock has the potential to do work by falling due to its position.
- Chemical Energy: Energy stored within the bonds of molecules. This stored power can be released through chemical reactions. Think of a battery or the fuel in a car.
- Thermal Energy: Associated with the temperature of a system. The hotter something is, the more thermal energy it has. This energy is related to the random motion of atoms and molecules.
- Radiant Energy: Energy transmitted as electromagnetic waves. Light and heat from the sun are good examples.
- Electrical Energy: The energy of moving electric charges. This is the form of energy used to power our homes and appliances.
Conservation of Energy: The Law That Governs Everything
Now, let’s delve into the heart of the matter: the law of conservation of energy. This principle, one of the most fundamental laws in physics, states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another. This means that the total amount of energy in a closed system remains constant.
Consider these scenarios to better grasp how the law of conservation of energy applies in real-world situations:
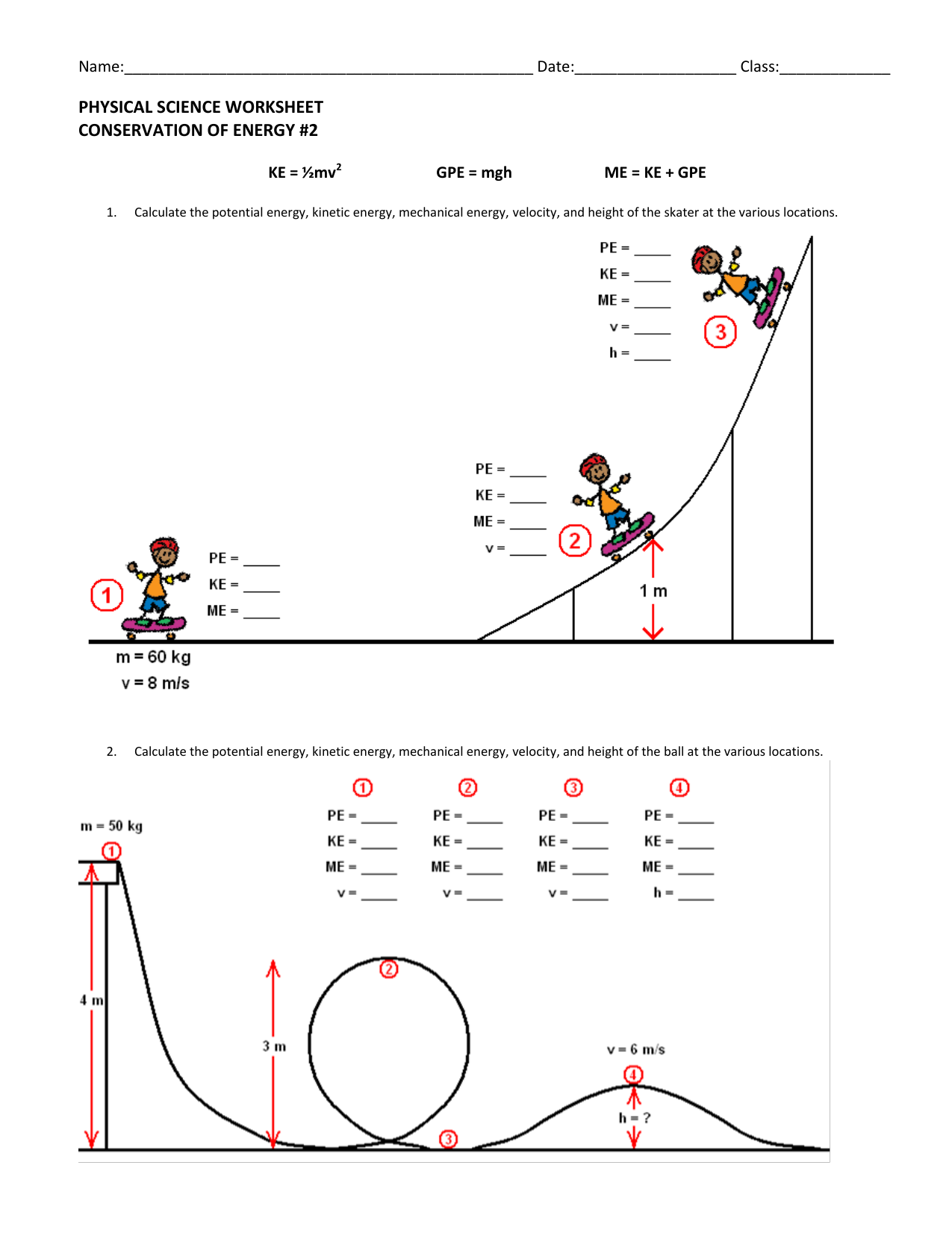
Image: wordworksheet.com
Real-World Examples
- A Swinging Pendulum: A pendulum swings back and forth. At its highest point, its potential energy is at a maximum, while its kinetic energy is zero. As it swings downward, the potential energy is transformed into kinetic energy, reaching maximum kinetic energy at the lowest point. The total energy of the swinging pendulum (potential + kinetic) remains constant.
- A Bouncing Ball: When a ball bounces, it falls and gains kinetic energy. Upon hitting the ground, the kinetic energy is partially converted into thermal energy (heating up the ball and the ground), and partially converted back into potential energy as the ball rises back up. The total energy is conserved, but some gets dissipated as heat.
- A Hydroelectric Dam: A hydroelectric dam uses the potential energy of water stored at a higher elevation. As the water flows downward, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, which then drives turbines to generate electricity. The total energy remains constant, but it’s transformed from potential energy to kinetic energy to electrical energy.
Conservation of Energy Worksheet Answer Key: Demystifying the Concepts
Finally, let’s turn our attention to what you have been waiting for: the Conservation of Energy Worksheet Answer Key. This worksheet serves as a practical tool to solidify your understanding of this fundamental law. It’s likely to be filled with problems, scenarios, and questions applying the principles of energy conversion and transformation. Since we’re focusing on answering questions on conservation of energy, we’ll delve into a few common types of problems you may encounter:
Example Questions and Answers
Here’s how you might approach addressing common types of questions on a conservation of energy worksheet.
Calculating Kinetic and Potential Energy
- Question: A ball with a mass of 0.5 kg is dropped from a height of 10 meters. What is the ball’s potential energy at the top, and what is its kinetic energy just before it hits the ground?
- Answer:
- Potential Energy: PE = mgh (where m is mass, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is height). PE = (0.5kg)(9.8m/s2)(10m) = 49 Joules.
- Kinetic Energy: At the bottom, all potential energy has been converted to kinetic energy. So, the kinetic energy is also 49 Joules.
Energy Transformation
- Question: A gas stove uses chemical energy from natural gas to heat water. Describe the energy transformations involved.
- Answer: The chemical energy in the natural gas is transformed into heat energy (thermal energy) by the burning process. This heat energy then transfers to the water, causing it to heat up.
Energy Efficiency
- Question: A lightbulb has an efficiency of 10%. What is the energy wasted as heat for every 100 Joules of electrical energy used by the lightbulb?
- Answer: If the efficiency is 10% that means 10% of the energy is used to produce light, and the remaining 90% is wasted as heat. So, 90 Joules are wasted.
Solving Problems
Remember, many problems in conservation of energy worksheets will involve solving for an unknown variable. The key to tackling them is setting up the correct equation to reflect the principle of energy conservation. The equation states that the total energy before an event equals the total energy after the event, though it may be distributed in different forms.
Example: A ball is thrown upward with an initial kinetic energy of 20 Joules. It reaches a maximum height of 5 meters. What is the potential energy at its highest point?
Solution:
- Initial kinetic energy = 20 J
- At its highest point, all kinetic energy is converted to potential energy.
- Therefore, potential energy at the highest point = 20 J.
Beyond the Worksheet: Real-World Applications
The Conservation of Energy worksheet answer key is not merely a tool for completing homework assignments. It’s a gateway to understanding how this principle impacts our daily lives and shapes the world around us. From renewable energy technologies to energy conservation in our homes, the law of conservation of energy guides innovation and sustainability.
Here are just a few examples of how this fundamental law is shaping our world:
Renewable Energy Technologies: Harnessing Nature’s Power
Renewable energy technologies, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric, rely on the principle of energy conservation. These technologies capture and transform natural energy sources like sunlight, wind, and water flow into usable electricity, demonstrating that energy is never lost, only transformed.
Energy Efficiency: Conserving Resources for a Sustainable Future
Energy efficiency seeks to minimize wasted energy in our homes, industries, and transportation systems. By improving the efficiency of appliances, vehicles, and buildings, we effectively reduce the amount of energy needed to perform the same tasks, leading to less reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating environmental impact.
Conservation Of Energy Worksheet Answer Key
Conclusion: Opening the Doors to Understanding
Conservation of energy is a fundamental principle that governs the world around us. By understanding this concept, we gain a deeper insight into how energy is transferred and transformed. The Conservation of Energy Worksheet Answer Key serves as a valuable tool to solidify your understanding of this essential principle, empowering you to tackle problems, analyze scenarios, and make informed decisions in a world driven by energy.
Beyond the classroom, the law of conservation of energy informs our understanding of the natural world, our technologies, and our impact on the environment. It is a principle that inspires us to seek out sustainable solutions, reduce energy waste, and harness the power of nature responsibly for a brighter future. So, open the doors to understanding, explore the world of energy conservation, and start making a difference!






